AI-assisted search 101: How AI is reshaping the way we find information
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is significantly changing how we search for information online. Until recently, the search experience usually involved entering queries into Google and manually reviewing results. AI-assisted search has changed the game. Users are now given enhanced results directly through their chosen AI platform and often won't click through to a source website. In this 101, we'll look at the basics of AI search and how you can future-proof your content for this emerging trend.
Examples of AI-assisted search
AI-assisted search comes in a few forms. Some are native apps, and others are browser-based; however, the overall experience and outcomes are essentially the same. Here are a few examples:
Arc Browser: Arc Browser integrates AI directly into your browsing experience. Instead of sifting through multiple links, Arc summarises key insights directly from search results, providing concise answers and relevant context. It presents content natively in the application UI, using emojis and snippets from sources to generate a unique "page" for the query results.
Perplexity: Perplexity offers a similar experience to Arc. It summarises web content and transparently cites sources, enabling verification and encouraging deeper exploration of topics.
Google AI Overviews: Google actively incorporates AI into its search functionality via the AI Overviews at the top of the results page. This provides a curated response to a user search and draws from relevant sources.
Microsoft Bing Chat: Bing Chat combines conversational AI with search functionality. Users can pose queries naturally, and Bing provides detailed, conversational responses, summarising multiple sources and offering follow-up question suggestions.
ChatGPT Browser Extension: The ChatGPT browser extension summarises search results directly, offers contextual answers to queries, and reduces the need for clicking through multiple websites.
AI-assisted search as standard, not optional
Smartphones are rapidly incorporating native AI capabilities into their operating systems. Features like Google's Assistant and Apple's Open AI-enhanced Siri demonstrate this shift. These tools proactively suggest information before users even initiate a search, learning from usage patterns and context. As this trend continues, AI-assisted search becomes less about user preference and more the default method of interacting with information digitally.
How AI-assisted search works
AI-assisted search makes finding information more straightforward and intuitive by understanding you better or delivering the illusion to the user that this is happening. Instead of requiring specific keywords, it lets you search naturally - as if you're chatting with another person. Here are a few of the technical features driving AI search:
Natural Language Processing - Understanding your words
Natural Language Processing, or NLP, helps the search understand everyday human language. This means you can ask questions how you'd normally speak or type, and the AI works out exactly what you're after—even when you're unsure how to phrase your query.
Machine Learning - Learning what you need
Machine Learning allows the search tool to improve every time it's used. By noticing patterns—like which results people select most often—it becomes more intelligent and personalised over time, anticipating your behaviour and progressively offering more relevant information.
Semantic Search - Getting the meaning right
Semantic search goes beyond just matching words. It understands the context and intent behind your question, so even if your exact search terms aren't found, you'll still receive helpful, closely related answers. Google has been doing this for a while, but AI search can take it further by asking questions to clarify your search intent.
What AI assisted results look like
To demonstrate how AI search agents display queries to a user, I've picked Arc Browser as a test case. Below, I've searched for "History course at LSE". The screenshots show how the AI behind the browser interprets source information and then displays it for the end user to consume.
Gathering sources
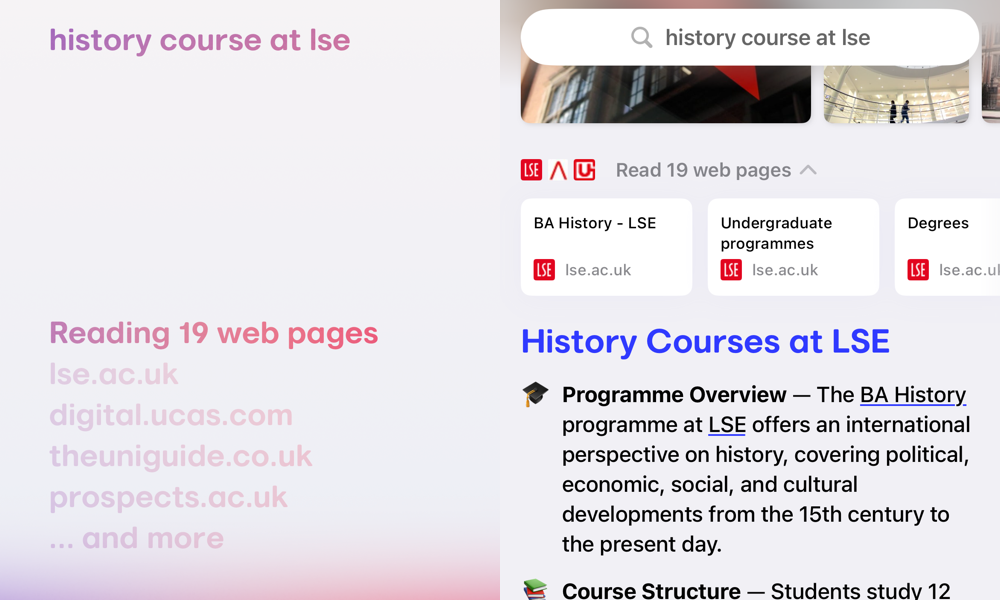
Arc takes the user query and checks it against primary sources (in this case the LSE course page for History BA) and then other relevant high quality sites. This means that the results are cross checked against a wide pool of data and not just a regurgitation of one source.
Presenting information

The way the browser presents results is closer to a webpage than a traditional search results listing. In this case, Arc has broken the content into sections which aid the user in consuming dense course information. These sections mirror the content presented on the source course page in a condensed form but with rich content pulled out, such as quotes and links to further reading.
What this means
The takeaway from this example, is that the results given here are of such a high quality that the user may not feel the need to click through to the source page. The dilemma here is that content creators can't know if their carefully crafted course page is being represented as intended, and that key or legally required information is being presented accurately.
In this specific case of a university course page, we know that the primary actions are either to sign up for an open day or apply for the course. At present, these call to actions aren't presented by the AI agent and there is a risk that end user may not know to click through to the institution site to carry out these actions.
Preparing for AI-assisted search is similar to making content accessible
Getting your content ready for AI-assisted search has much in common with making your website accessible. Both approaches involve structuring information so it's easy for machines and people to understand. Like accessibility relies on clear headings, meaningful descriptions, and organised content for screen readers, AI-assisted search tools depend on structured data and accurate markup to interpret and summarise content correctly.
By writing clearly, providing descriptive alt-text for images, and using semantic markup consistently, you're helping AI and users find exactly what they're looking for. Ultimately, what's good for accessibility also benefits AI-assisted search—and vice versa.
Benefits of AI-assisted search
- Efficiency: Quickly delivers precise answers, saving users time manually scanning results.
- Enhanced accuracy: Filters out irrelevant information, providing more targeted and relevant search results.
- Ease of use: Allows conversational, intuitive interactions, making search accessible for everyone.
- Improved accessibility: AI-assisted search can significantly enhance accessibility for users with disabilities by providing alternative ways of interacting with information, such as voice commands and auditory results.
SEO impact and the importance of structured data
As AI-assisted search grows, the importance of structured data becomes even more significant. Content creators must use schema markup and other structured data techniques to define content elements clearly. Properly structured data means that AI can accurately understand, index, and present the information, benefiting users and content providers.
Reduced website traffic and implications
One consequence of highly effective AI-assisted search is that users might never click through to the source websites. AI-generated answers often satisfy user queries without needing to visit the source, which can significantly reduce traffic and affect the visibility and revenue of websites reliant on advertising or visitor metrics.
If the data on websites is poorly structured or incomplete, AI tools may generate misleading or inaccurate summaries, negatively impacting both user experience and the reputation of content providers.
Challenges and considerations
While AI-assisted search provides benefits, a few issues need attention:
- Privacy: AI-driven search requires significant data collection, raising privacy concerns. Public sector organisations are cautious about sharing data with AI models due to risks of exposing sensitive information, uncertainty over data handling and transparency by AI providers, and potential legal and financial penalties under regulations like GDPR.
- Bias and fairness: AI algorithms can unintentionally perpetuate biases if not continuously monitored and adjusted.
- Transparency: The accuracy and trustworthiness of AI-generated results depend on clear sourcing and transparency. If users receive what they believe to be the answer to their query and never click through to the source, they won't verify the information is accurate.
Conclusion: Adapting today for tomorrow's AI-driven search
AI-assisted search isn't a distant possibility—it's already embedded into how we interact digitally. As AI integration moves from novelty to necessity, organisations and content creators must adapt proactively. Prioritising clear, structured, and accessible content enhances visibility and ensures your information remains authoritative and trustworthy.
Now is the time to optimise your digital presence for AI-driven search. Embrace best practices around structured data, natural language, and accessibility to position your content prominently in the age of AI.








